Understanding the differences between PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and rPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate) is essential in today’s world, where environmental sustainability is becoming increasingly important. PET and rPET are both widely used in various industries, but they differ in terms of their raw material source, manufacturing process, properties, and environmental impact.
In this article, we will delve into the distinctions between PET and rPET, shedding light on their characteristics, applications, and the implications of choosing one over the other. By gaining a deeper understanding of PET and rPET, we can make more informed decisions regarding plastic usage and contribute to a greener future. Let’s explore the world of PET and rPET, unraveling their unique attributes and the benefits they offer in terms of sustainability and resource conservation.
Contents
PET: Definition and Properties
PET, or Polyethylene Terephthalate, is a thermoplastic polymer that belongs to the polyester family. It is a versatile material widely used in various industries due to its excellent combination of properties.
PET plastic is produced through a polymerization process that involves the reaction of terephthalic acid or its ester with ethylene glycol. This process results in a polymer with a high molecular weight, making it strong, durable, and resistant to impact.
One of the key properties of PET is its clarity, which makes it suitable for transparent packaging applications. It has good barrier properties against moisture, gases, and odors, making it ideal for food and beverage containers. PET is also lightweight and has excellent dimensional stability, which allows for efficient transportation and storage of products.
Furthermore, PET is highly recyclable, which contributes to its environmental appeal. It can be easily identified by the recycling symbol with the number “1” inside it. The recycling process involves cleaning, shredding, and melting PET bottles, converting them into recycled PET flakes or pellets that can be used to manufacture new products.
In conclusion, PET is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its strength, clarity, barrier properties, and recyclability. Its versatility and environmental benefits have made it a popular choice in industries such as packaging, textiles, automotive, and more. Understanding the properties of PET sets the foundation for comparing it to rPET and evaluating their respective advantages and limitations.
rPET: Definition and Production Process
rPET, or Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate, refers to PET that has been recycled from post-consumer PET bottles or other sources. It plays a crucial role in the circular economy by reducing the reliance on virgin plastic production and minimizing plastic waste.
The production process of rPET involves several steps to transform used PET bottles into reusable material:
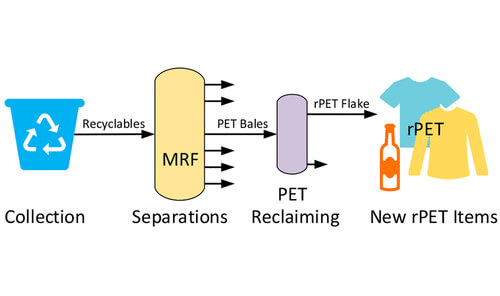
- Collection and Sorting: Post-consumer PET bottles are collected through recycling programs or waste management systems. These bottles go through a sorting process, where they are separated based on color and plastic type.
- Cleaning and Shredding: The sorted PET bottles are thoroughly cleaned to remove any impurities such as labels, caps, and contaminants. The bottles are then shredded into smaller pieces, known as flakes.
- Melting and Purification: The PET flakes are melted down and subjected to further purification processes. This includes removing any remaining impurities, such as paper labels or residual liquids, to ensure the resulting rPET is of high quality.
- Solidification and Pelletization: The purified molten rPET is solidified and transformed into small pellets or granules. These pellets can be used as a raw material for various applications, including the manufacturing of new PET products.
rPET offers several environmental benefits. By recycling PET bottles, it reduces the amount of plastic waste ending up in landfills or oceans. Additionally, the production of rPET consumes less energy and resources compared to the production of virgin PET. It also helps decrease the carbon emissions associated with the manufacturing of new plastic.
The adoption of rPET promotes the principles of a circular economy, where materials are recycled and reused, minimizing the demand for new resources and reducing environmental impact.
In conclusion, rPET is a recycled form of PET obtained from post-consumer PET bottles. The production process involves collection, sorting, cleaning, shredding, melting, purification, and pelletization. rPET contributes to waste reduction, conservation of resources, and decreased carbon emissions, making it an environmentally preferable choice compared to virgin PET. Understanding the production process of rPET allows us to appreciate its role in sustainable plastic usage and the circular economy.
Differences between PET and rPET
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and rPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate) have distinct differences in terms of their raw material source, manufacturing process, properties, and environmental impact. Let’s explore these differences in more detail:
A. Raw Material Source:
- PET: PET is derived from fossil fuels, typically petroleum or natural gas. It is produced from non-renewable resources.
- rPET: rPET is obtained from recycled PET bottles or other post-consumer sources. It relies on the recycling of plastic waste, reducing the need for virgin plastic production.
B. Manufacturing Process:
- PET: The manufacturing process of PET involves polymerization, where terephthalic acid or its ester reacts with ethylene glycol to create the polymer. It is a process that starts from scratch and requires the use of raw materials.
- rPET: The production process for rPET involves recycling PET bottles. It includes cleaning, shredding, melting, purification, and pelletization of the collected bottles. The recycling process transforms used PET into reusable material.
C. Properties and Quality:

- PET: PET has consistent and standardized properties. Its properties, such as clarity, strength, and barrier properties, are well-established and predictable.
- rPET: rPET properties may vary due to the recycling process. The quality of rPET can be influenced by factors such as the quality of the collected bottles, the effectiveness of the recycling process, and the presence of impurities or contaminants.
D. Environmental Impact:
- PET: PET production relies on the extraction and processing of fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. It has a higher carbon footprint compared to rPET.
- rPET: rPET reduces the demand for virgin plastic production, conserves resources, and decreases carbon emissions. It helps divert plastic waste from landfills or oceans, contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy.
Understanding these differences is essential in making informed choices about plastic usage. While PET has its applications and advantages, rPET offers environmental benefits through recycling and resource conservation. Considering the properties and environmental impact of PET and rPET allows us to evaluate their suitability in various industries and promote more sustainable practices.
Applications and Use Cases
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and rPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate) find applications in various industries. Let’s explore their respective uses and compare their performance in different scenarios:
A. PET Applications:
- Packaging: PET is widely used for packaging applications, including bottles for beverages, water, juices, and personal care products. Its clarity, lightweight nature, and excellent barrier properties make it suitable for preserving the freshness and integrity of the packaged products.
- Textiles: PET is utilized in the textile industry to produce polyester fibers, which are used to make clothing, upholstery, and carpets. It offers durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties.
- Electrical and Electronics: PET is used for insulation in electrical cables, wiring, and electronic components due to its electrical properties and heat resistance.
- Automotive: PET is employed in the manufacturing of automotive parts, such as interior trims, seat fabrics, and carpets, due to its durability and resistance to chemicals and UV radiation.
B. rPET Applications:
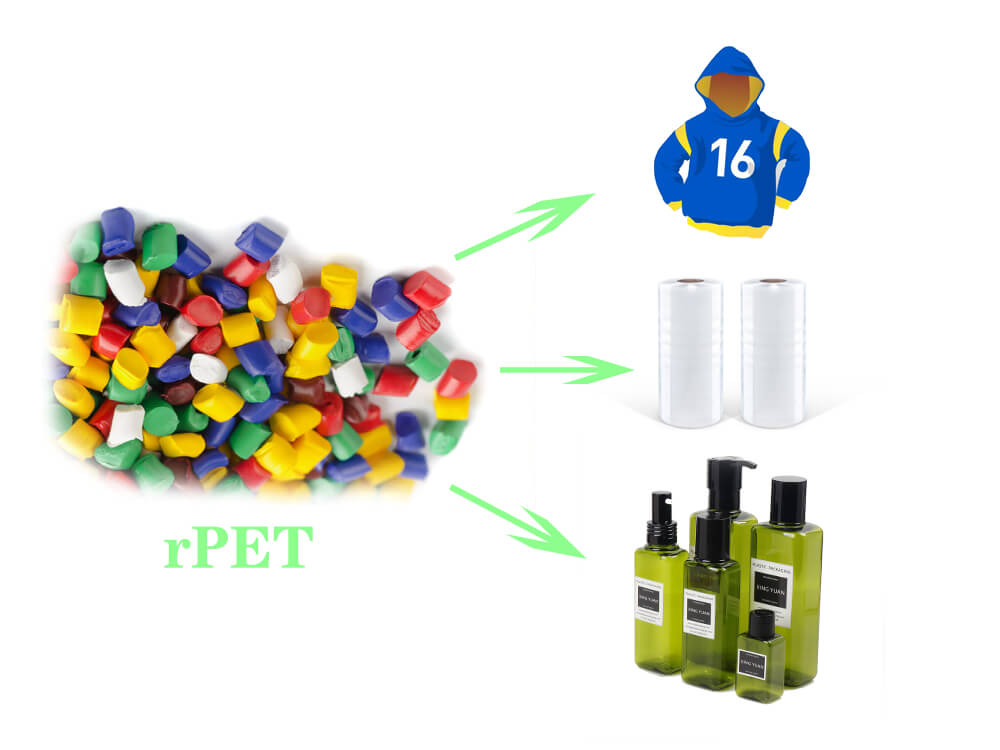

- Packaging: rPET is increasingly used in packaging applications, especially for food and beverages. It offers the same properties as PET but with the added benefit of reduced environmental impact. Companies are adopting rPET for bottles, trays, and other packaging materials.
- Textiles: rPET is used to produce recycled polyester fibers, which are then used in clothing, sportswear, and home textiles. The demand for sustainable fashion has fueled the adoption of rPET in the textile industry.
- Construction: rPET can be used in construction materials, such as insulation, roofing, and flooring, providing both performance and environmental benefits.
- Other Industries: rPET finds applications in industries like automotive, electronics, and household goods, where the use of recycled materials aligns with sustainability goals.
Comparing PET and rPET applications, it is evident that both materials have versatile uses. However, rPET is gaining traction due to its sustainable attributes and increased consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. As technologies advance and awareness grows, rPET is expected to find wider adoption across various industries.
Understanding the specific applications and use cases of PET and rPET allows us to assess their suitability, environmental implications, and contribute to the development of a more sustainable and circular economy.
Considerations and Future Trends
As the world becomes more conscious of the environmental impact of plastic usage, considerations and future trends related to PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and rPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate) are emerging. Let’s explore some key aspects to consider and the potential trends for these materials:
A. Consumer Awareness and Demand:
- Growing Awareness: Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental issues associated with plastic waste and are seeking sustainable alternatives.
- Demand for Sustainable Packaging: There is a rising demand for products packaged in eco-friendly materials like rPET. Consumers are actively supporting brands that prioritize sustainability.
B. Technological Advancements:
- Improved Recycling Technologies: Technological advancements in recycling processes are enhancing the quality and efficiency of rPET production. Advanced sorting, cleaning, and purification techniques are being developed to yield high-quality rPET with consistent properties.
- Innovation in Material Performance: Research and development efforts are focused on improving the properties of rPET to match or surpass those of PET. This includes advancements in strength, clarity, and barrier properties.
C. Legislative Measures and Industry Initiatives:
- Plastic Bans and Regulations: Governments and regulatory bodies are implementing bans and regulations on single-use plastics, encouraging the use of recycled and sustainable materials like rPET.
- Industry Commitments: Many companies are committing to using a certain percentage of recycled content in their packaging or products. These initiatives are driving the demand for rPET and fostering a circular economy.
D. Packaging Design and Waste Management:
- Design for Recycling: Companies are focusing on designing packaging that is more easily recyclable. This includes using mono-materials and eliminating complex or mixed-material packaging that hinders recycling.
- Improved Waste Management Infrastructure: Investments in waste management infrastructure, such as recycling facilities and collection systems, are crucial to increase the recycling rates of PET and rPET.
The future trends for PET and rPET point towards a shift towards more sustainable practices and materials. The adoption of rPET is expected to continue to grow as technology advancements improve its properties and production processes. Furthermore, collaboration between industries, governments, and consumers will play a vital role in driving the transition to a more circular and sustainable plastic economy.
By considering these factors and embracing innovative approaches, we can accelerate the shift towards a greener future, reduce plastic waste, and preserve our environment for generations to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between PET and rPET is crucial for making informed decisions about plastic usage. PET, derived from fossil fuels, offers standardized properties and is widely used in packaging, textiles, and automotive industries. On the other hand, rPET, obtained from recycled PET bottles, reduces waste, conserves resources, and mitigates environmental impact.
As consumer awareness grows and demand for sustainable practices increases, rPET is gaining momentum as a preferred choice for packaging and other applications. Technological advancements, legislative measures, and industry initiatives are driving the adoption of rPET and promoting a circular economy.
By embracing the advantages of rPET and supporting initiatives that prioritize sustainability, we can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. It is our collective responsibility to make conscious choices and promote the use of recycled materials like rPET, thereby reducing plastic waste and preserving our environment.





