Are we truly aware of the impact our beauty products have on the environment? How can we make a difference in the cosmetics industry while still looking our best? These questions drive us to explore sustainable solutions in cosmetic packaging. In an era where environmental consciousness is paramount, adopting eco-friendly practices is not only a responsibility but also an opportunity for positive change.
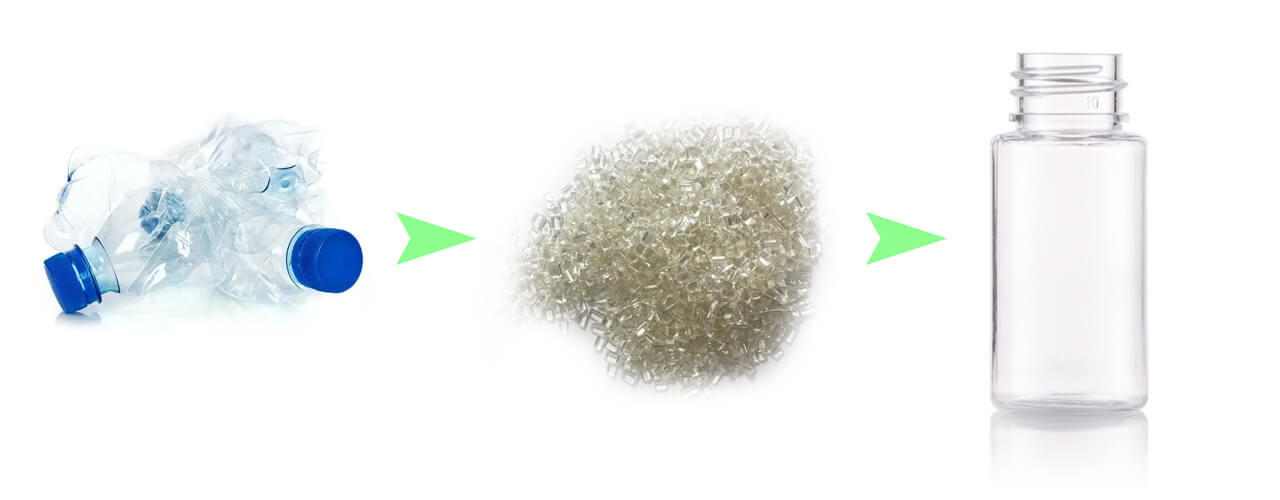
Welcome to the world of PCR (Post-Consumer Recycled) production in cosmetic packaging. PCR production offers a promising solution that combines innovation and environmental stewardship. By repurposing post-consumer materials, we can reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize our carbon footprint.
In this article, we will delve into the principles and process behind PCR production. We will explore the careful selection and collection of post-consumer materials, the rigorous sorting and cleaning procedures, and the transformative manufacturing techniques that turn PCR materials into packaging bottles. Furthermore, we will shed light on the benefits and applications of PCR in cosmetic packaging, showcasing how it aligns with sustainability goals and consumer demands.
Join us on this journey towards a greener future as we uncover the world of PCR production in cosmetic packaging. Together, we can redefine beauty standards while preserving our planet for generations to come.
Contents
Principles of PCR Production:
PCR (Post-Consumer Recycled) production in the cosmetics industry is guided by key principles that promote sustainability and environmental responsibility. By adhering to these principles, cosmetic packaging manufacturers can make a significant impact on reducing waste and contributing to a circular economy.
A. Source Selection and Collection of Post-Consumer Materials:
The first principle of PCR production lies in the careful selection and collection of post-consumer materials. Collaborations with recycling centers and waste management facilities allow for the acquisition of plastic bottles and containers that have reached the end of their life cycle. By diverting these materials from landfills, we can transform waste into valuable resources.
B. Sorting and Cleaning Processes for Quality Control:
The next principle revolves around the sorting and cleaning processes. Advanced technologies are employed to accurately separate different types of plastics and remove contaminants effectively. Through meticulous sorting and thorough cleaning, the PCR materials are purified, ensuring that only high-quality materials proceed to the next stage of production.
C. Manufacturing Techniques to Transform PCR Materials:
The transformation of PCR materials into packaging bottles is a crucial step in PCR production. Innovative manufacturing techniques are employed to process the recycled materials, creating packaging products with the same functionality and aesthetics as virgin plastic. These techniques include melting, molding, and shaping the PCR materials into various bottle designs, caps, and closures.
D. Testing and Validation Procedures for Safety and Compliance:
The final principle of PCR production focuses on rigorous testing and validation. PCR packaging undergoes comprehensive tests to ensure its safety, durability, and compliance with industry standards. These tests encompass assessments for chemical resistance, product stability, and adherence to regulatory requirements. By prioritizing these tests, PCR packaging is guaranteed to meet the highest quality and safety standards.
By adhering to these principles, cosmetic packaging manufacturers can contribute to a more sustainable future. PCR production reduces waste, conserves resources, and promotes responsible consumption. In the next section, we will delve into the detailed process involved in PCR production, shedding light on each step from material sourcing to the final packaging product.
Process of PCR Production:
The process of PCR (Post-Consumer Recycled) production involves several essential steps that transform post-consumer materials into eco-friendly packaging bottles. Let’s take a closer look at each stage, from material sourcing to the final product.
Step 1: Collection
Plastic waste is collected from various sources, including households, businesses, and recycling centers. This can be done through curbside collection, drop-off points, or specialized recycling programs.
Step 2: Magnetic Separation
The collected plastic waste is subjected to a magnetic separator. This device uses magnets to attract and separate any ferrous materials, such as iron or steel, which may be present in the waste stream. This step helps remove metal contaminants that could interfere with the recycling process.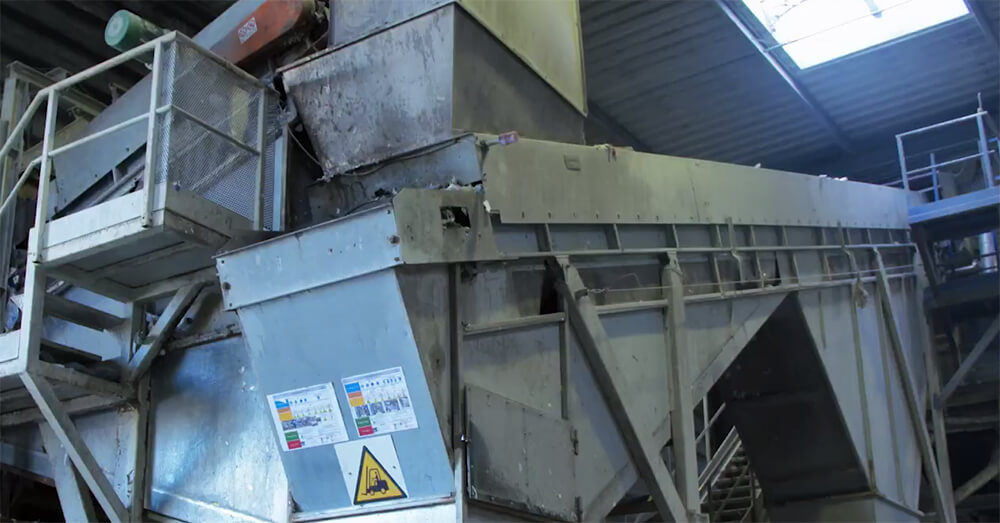
Step 3: Sorting
After magnetic separation, the plastic waste is sorted based on its type and quality. Manual or automated sorting systems are employed to separate different types of plastics, such as PET, HDPE, PVC, and others. Optical sorting machines, infrared sensors, or manual inspection may be used to identify and segregate the plastics accurately.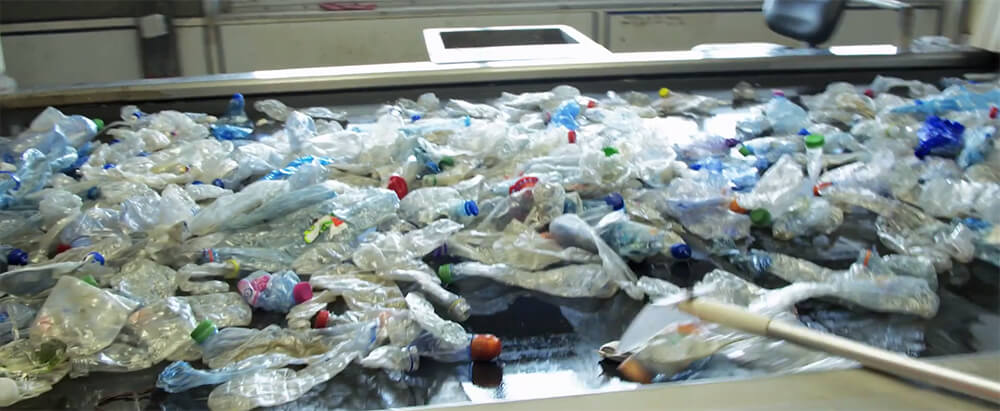
Step 4: Shredding
Once the sorting process is complete, the plastic waste is shredded into smaller pieces or flakes. Shredding machines or granulators are utilized to break down the plastic into manageable sizes. This step increases the surface area of the plastic, making it easier to clean and process further.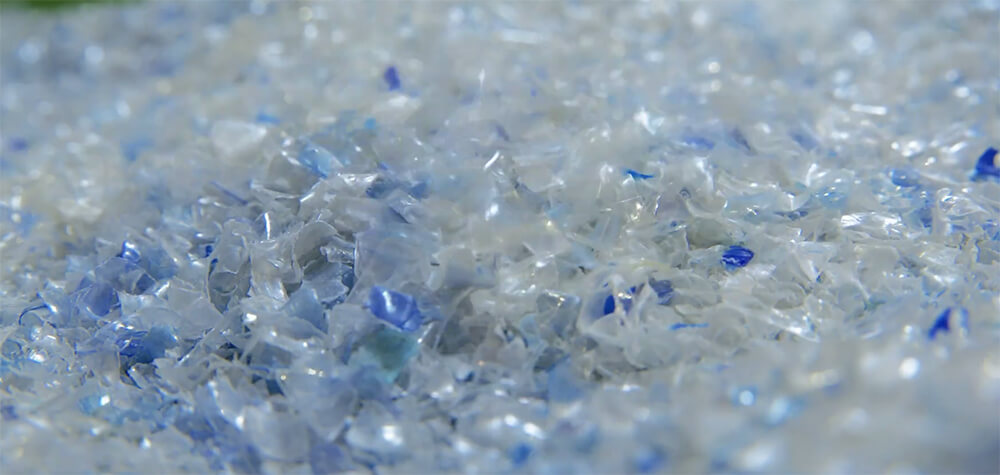
Step 5: Cleaning
The shredded plastic flakes undergo a thorough cleaning process to remove impurities, contaminants, and residues. The cleaning process typically involves a combination of mechanical agitation, water, and detergents. The plastic flakes are washed, rinsed, and sometimes subjected to additional treatments to ensure the removal of dirt, labels, adhesives, and other contaminants.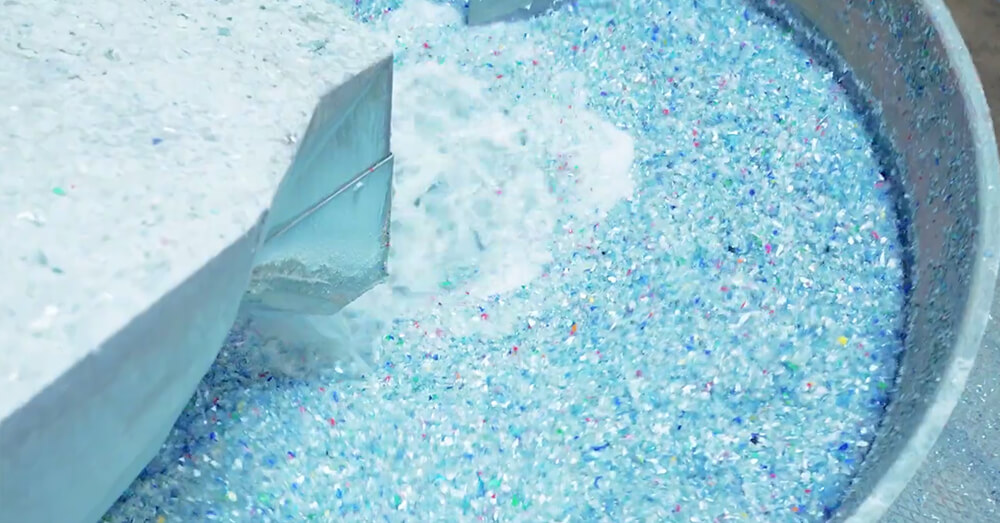
Step 6: Drying
Following the cleaning process, the plastic flakes are dried to eliminate any remaining moisture. Various drying techniques can be employed, such as hot air drying, centrifugal drying, or vacuum drying. This step is crucial to prevent moisture-related issues during the subsequent melting process.
Step 7: Melting
The dried plastic flakes are melted down in an extruder or a melting furnace. The flakes are fed into the machine where they are subjected to heat and mechanical forces. The combination of heat and pressure causes the plastic to melt into a molten form, ready for further processing.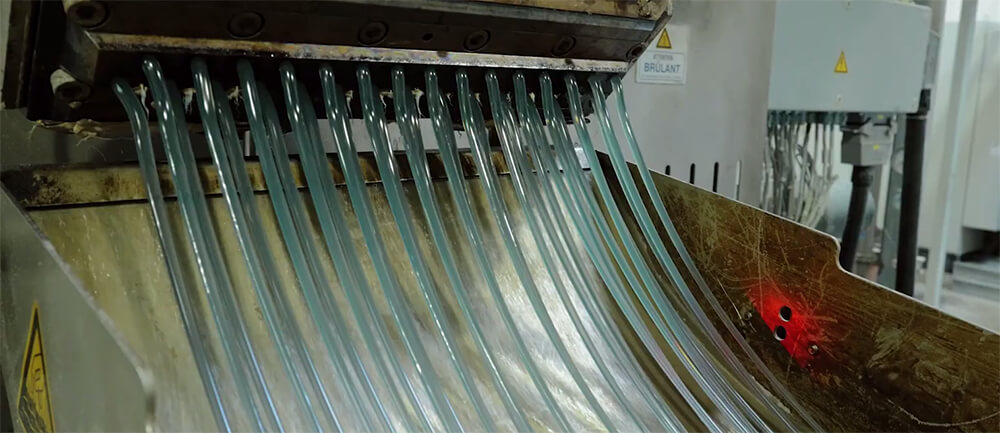
Step 8: Granulation
Once melted, the molten plastic is forced through a die to form small pellets or granules. The molten plastic is extruded through the die, which shapes it into a specific cross-sectional profile. As the extruded plastic comes into contact with a cooling medium, it solidifies and is cut into pellets or granules of uniform size. These plastic pellets can be easily handled, transported, stored, and used as raw material for manufacturing new plastic products.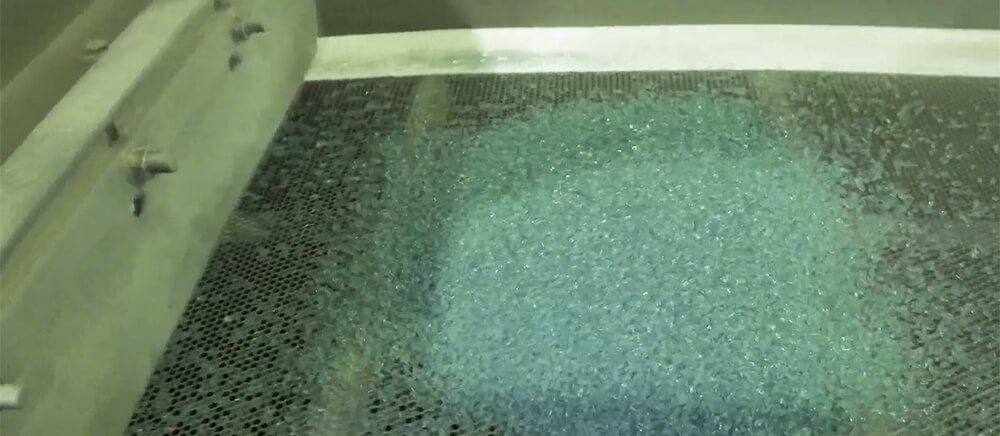
By following this process, PCR production not only reduces waste and conserves resources but also delivers packaging solutions that meet the highest quality standards. The commitment to sustainability and the adoption of PCR packaging in the cosmetics industry contribute to the preservation of the environment and pave the way for a more sustainable future.
In the next section, we will explore the benefits and impacts of PCR production, shedding light on the environmental, economic, and social advantages of incorporating PCR packaging in the cosmetics industry.
Benefits and Impacts of PCR Production:
PCR (Post-Consumer Recycled) production in the cosmetics industry brings forth a multitude of benefits and impacts, encompassing environmental, economic, and social aspects. Let’s delve into these advantages and explore the positive changes that PCR packaging can bring.
A. Environmental Benefits:
- Waste Reduction: PCR production significantly reduces waste by repurposing post-consumer materials that would otherwise end up in landfills or incinerators. By diverting these materials, we minimize the strain on natural resources and mitigate the environmental impact of plastic waste.
- Resource Conservation: PCR production conserves valuable resources such as petroleum, water, and energy. By utilizing recycled materials, we reduce the need for virgin plastics, helping to preserve natural resources for future generations.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Manufacturing PCR packaging requires less energy compared to producing packaging from virgin materials. This results in reduced carbon emissions and a lower overall carbon footprint, contributing to the fight against climate change.

B. Economic Benefits:
- Cost-effectiveness: PCR production offers cost advantages by utilizing recycled materials, which can be more cost-effective compared to virgin plastics. This allows companies to achieve sustainable practices while maintaining competitiveness in the market.
- Resource Efficiency: By reducing dependence on virgin materials, PCR production promotes resource efficiency, leading to long-term cost savings. Additionally, the circular economy approach of PCR encourages a more efficient use of resources throughout the value chain.
C. Social Impacts:
- Circular Economy Promotion: PCR production aligns with the principles of a circular economy, fostering a sustainable and regenerative system. By closing the loop on plastic waste, we contribute to the creation of a more sustainable society.
- Consumer Awareness and Engagement: The use of PCR packaging raises consumer awareness about the importance of recycling and sustainable choices. It empowers consumers to make environmentally conscious decisions by opting for products packaged in PCR materials.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: PCR production encourages collaborations between cosmetic companies, recycling centers, and waste management facilities. This collaboration strengthens partnerships, fosters innovation, and supports the development of sustainable practices throughout the industry.
By embracing PCR production in cosmetic packaging, we can achieve tangible environmental benefits, realize economic advantages, and foster positive social impacts. These benefits create a ripple effect, inspiring other industries and consumers to adopt sustainable practices and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, PCR (Post-Consumer Recycled) production revolutionizes the cosmetics industry, offering a sustainable solution for packaging needs. By embracing the principles and process of PCR production, companies can contribute to waste reduction, resource conservation, and a greener future.
Choosing PCR packaging demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility and resonates with conscious consumers who prioritize sustainable products. Our company takes pride in supplying a wide range of PCR cosmetic bottles, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly packaging options.
Together, let us embrace PCR production and drive positive change in the cosmetics industry. By making responsible choices, we can create a lasting impact on the environment, promote a circular economy, and ensure a brighter and more sustainable future for all.
Xingyuan Plastic supplies various PCR cosmetic bottles. Contact us for more information about PCR and cosmetic packaging.